Abstract
The development of Bluetooth technology has had a revolutionary effect on simplifying everyone’s lives, erasing the need for wires. When this concept was first introduced, engineers recognized that this technology could be applied to a variety of devices. From there, they tested it on headphones, ultimately transforming the technology as a whole. Wireless headphones began to take over the audio device market, with every tech company producing their own version with Bluetooth capability. Wired headphones could soon become obsolete.
Introduction
Imagine this: you are getting ready to listen to that new hit song from your favorite artist, your excitement builds, and you do whatever it takes to set the mood and give yourself the ultimate listening experience. You close all the doors and windows and turn off all noisy things in your room. You reach for your pocket to pull out your wired earbuds, only to discover that they are once again all tangled up, ruining the perfect ambiance of your listening experience. Now that you have untangled them, you are listening to your music and want to get comfortable, so you decide to move to your bed. But your earbuds are connected to your computer and now you are stuck listening to the music at your desk. These are just some of the common problems that users of wired earbuds face. Nowadays, people are opting for the more user-friendly wireless earbuds, as wired headphones slowly phase out.
How Wired Headphones Work
Headphones essentially work the same way that a battery powers a lightbulb. The battery provides electricity to the light bulb using two wires on both ends. Electricity flows out from the negative end and in through the positive end, completing the circuit. In headphone, the cord connecting the headphones to the smartphone contains inner wires, allowing an electrical current to run through it in either direction. In order to complete the circuit, the smartphone acts as a “battery” for the headphones. The smartphone sends electrical energy to the headphones, where it is received in a small coil. The headphones act as a miniature speaker and turn the electrical energy into sound using the coil’s magnetic force to vibrate the air, effectively creating sound.
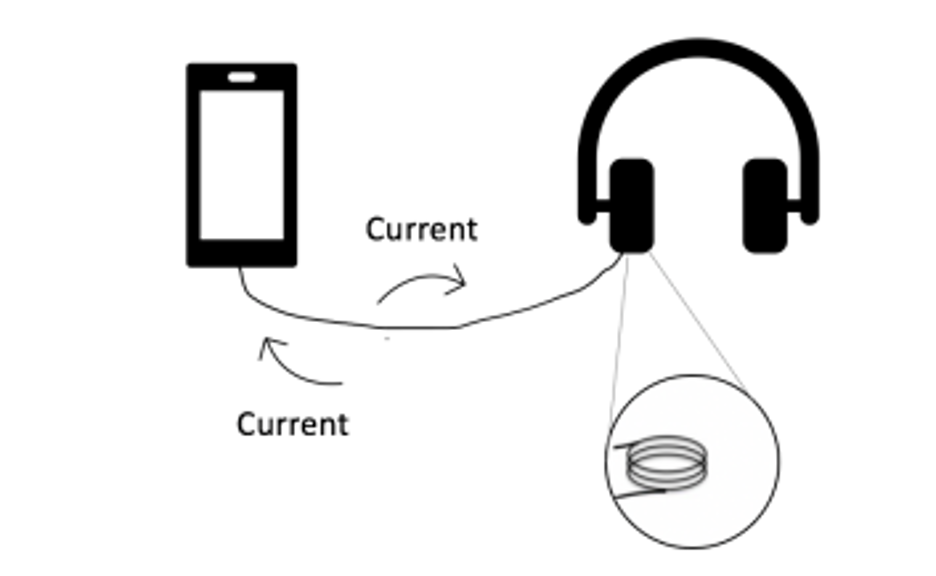
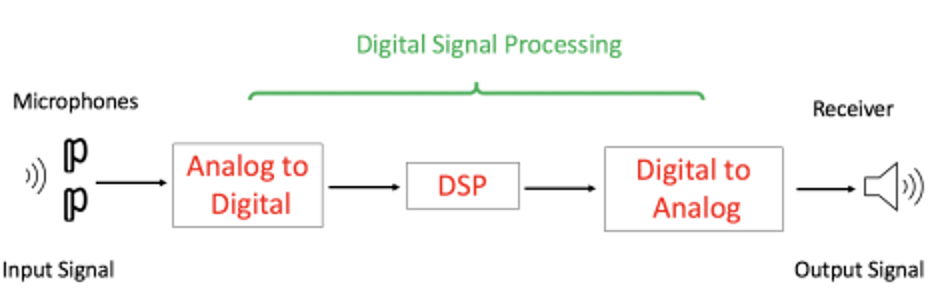
Electrical energy provided by the smartphone is a type of digital signal, which represents data as a sequence of discrete values. The smartphone contains digital audio, also known as bits. Bits are a series of 0s and 1s that serve as the building blocks of computer language. Headphones contain a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that transforms the digital data and signals into analog audio signals. Digital-to-analog converters are devices that receive digital data as a series of numbers and output a voltage proportional to the value of its digital data. These devices are key components in the production of audio. Analog signals are continuous signals that convey the signal’s information. In this case, the signals are conveyed as audio. When audio is played, bits are sent through the digital-to-analog converters, creating the analog signals. The analog signals are then sent through the wires and into the headphones.
Then, the analog signals are received in the headphone’s driver units. The units are found in each ear cup and contain two types of magnets and an electromagnetic coil that work together to deliver sound. One magnet is fixed in place, while the other is an electromagnet that moves within the earcup. The electromagnet moves back and forth according to the bit’s pattern of 0s and 1s. This causes it to be repelled and attracted to the fixed magnet, making it vibrate. The vibration of the electromagnet causes the air surrounding it to vibrate, creating sound. The speed at which it vibrates creates pitch. When you adjust the volume on the headphones, the vibration speeds will adjust accordingly. Fast vibrations create high pitch sounds, while slow vibrations create low pitch sounds.

Bluetooth Technology
Compared to wired headphones, the main feature that distinguishes wireless ones is the absence of the cords. The cords ensure that there is a secure connection from the device to its headphones. Developers decided to use Bluetooth to connect these smart devices to the headphones. The rise of this technology has simplified the sharing of data between devices and allows users to do things, such as making a phone call or listening to music, much easier.
Bluetooth is the wireless communication technology that enables a variety of devices to work together across a small distance. All Bluetooth devices have a chip that can encode, decode, and transmit data. These devices send out pinging signals that are detected by other Bluetooth devices. Once the user accepts it, a Bluetooth connection is established, linking the two devices together. This is also known as a piconet, which is a mini-network of radio waves communicating back and forth between the paired devices. The waves are relatively short, preventing the Bluetooth waves from going all over the place.
Bluetooth signals hop around on different frequencies at a rate of 1,600 times per second [2]. This movement is known as frequency-hopping spread spectrum, and keeps the Bluetooth signal connected between all paired devices. Additionally, it prevents static from occurring due to the clashing signals and keeps the connection super secure. The main reason Bluetooth has been so prominent in modern technology is because it requires very little power to operate. Radio waves have a short broadcasting range and data streams have been optimized to communicate as little as necessary. New Bluetooth technology even offers low power modes that allow for connection with Bluetooth devices even if there is no power at that moment.
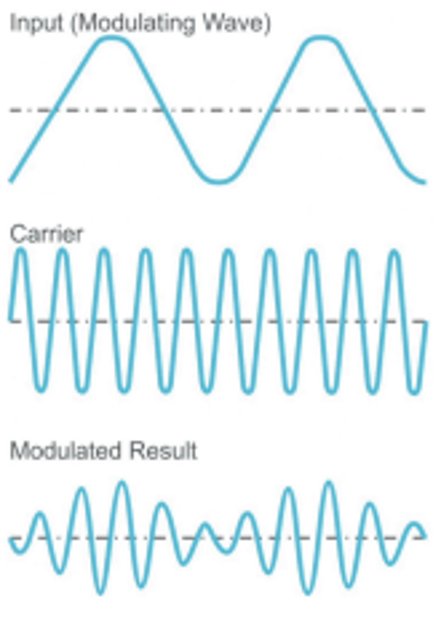
Bluetooth technology is becoming increasingly popular, so much so that headphone technology has found success in their incorporation of Bluetooth into their products, paving the way towards a new wireless future. To understand how Bluetooth was implemented into headphones, we must take a look at how wireless communication and technology works. Wireless communication transmits radio frequency waves from point A to point B. Point A is known as the transmitter and point B refers to the receiver. The process in which these waves are transmitted is called modulation. Modulation describes how input data is converted into radio waves by adding information to carrier signals [3]. Carrier signals are waveforms that carry out and convey information. During the modulation process, information is encoded and transmitted through space at the speed of light.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The main appeal in wireless headphones is the freedom to use them wherever you go. For example, if you want to listen to music while you are jogging, wireless headphones are the way to go. The headphones will not weigh you down and they fit snugly in your ear. With the power of Bluetooth technology, wireless headphones can access a variety of features that their wired counterpart is incapable of. For example, Apple AirPods allow users to give commands to its virtual assistant, Siri, using its wireless charging case, and even play and pause your audio by double tapping on the earphones. On top of that, wireless headphones are capable of connecting to any Bluetooth-enabled device, such as the Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra, PlayStation 4, and even Alexa speakers. On the other hand, while wired headphones can connect to the majority of devices, some of the newer smartphone devices have changes in their design, where they would require an extra accessory in order to utilize the wired headphones. With all of these extra features, wireless headphones tend to be much more expensive than wired ones, ranging anywhere from $100 to $500. In terms of connectivity, there is a possibility that users will encounter interferences when connecting their wireless headphones to their devices. Since Bluetooth uses the same frequency as other Wi-Fi devices, other devices that are using the same Wi-Fi network may prevent you from having a consistent listening experience.
There are a variety of advantages and disadvantages to consider for wired headphones. The main benefit of wired headphones is their superior sound quality, due to their directly receipt of analog signals through their cords. Analog signals have the power to handle more data than Bluetooth, allowing them to produce better sound quality. Wired headphones also do not require a battery supply, letting users use them whenever and wherever they would like. However, the main problem that consumers have with them comes from the cords themselves. Using them can be sufficient for those who aren’t always on the move, but the length of the cord limits the user’s range of movement and can get in the user’s way. They can be problematic at times because they can get tangled up easily when they are not stored appropriately [5]. Thus, while wired headphones may lack features that wireless headphones possess, they are proven to be the most cost-effective option and will provide you with the bare essentials to have a quality listening experience.
Which Wireless Technology is For You?
With consistent improvements in Bluetooth technology, it’s clear that wireless headphones are here to stay. Advanced technology has improved the overall listening experience for users, specifically in offering superior sound quality, improved noise cancellation technology, and new hands-free control methods allowing users to do things such as changing songs or activating noise cancellation. With technology companies looking to invest into developing the best wireless accessories, it begs to raise the question: which wireless accessory is best for us? Generally, we consider looking at prices, sound quality, and other features before making a decision on which type of headphone to purchase [6].
Wireless headphones come in three distinct styles: over-ear, on-ear headphones, and in-ear earphones [7]. Over-ear headphones are the biggest of the three, intended for use at home or work. These types of headphones are not meant to be portable, but have a very comfortable fit as the earcups and headband are well-padded. These models have the largest driver units, giving users the ultimate listening experience. Their oversized earcups completely enclose your ears, blocking out all noise and preventing sounds from leaking. These types of noise-cancelling headphones will help you focus and relax. Thus, over-ear headphones can provide the best sound quality and performance to its users.
In-ear earphones, or “earbuds”, are the most commonly used. Due to their small size, they are extremely portable and can be simply tossed in your bag or pocket. Generally, these options are comfortable, but can occasionally be irritating depending on the ear-tip’s materials and how long the user wears them. However, for activities such as exercising, they are the best options due to their portability and ability to fit snugly in your ear. With its snug fit, earphones will isolate you from the majority of outside noises, allowing you to tune out the noises and enjoy your listening experience. As a result of their small size, these earbuds will have smaller driver units, meaning they are not capable of producing a high range of sound frequencies as compared to the on-ear and over-ear versions.

Conclusion
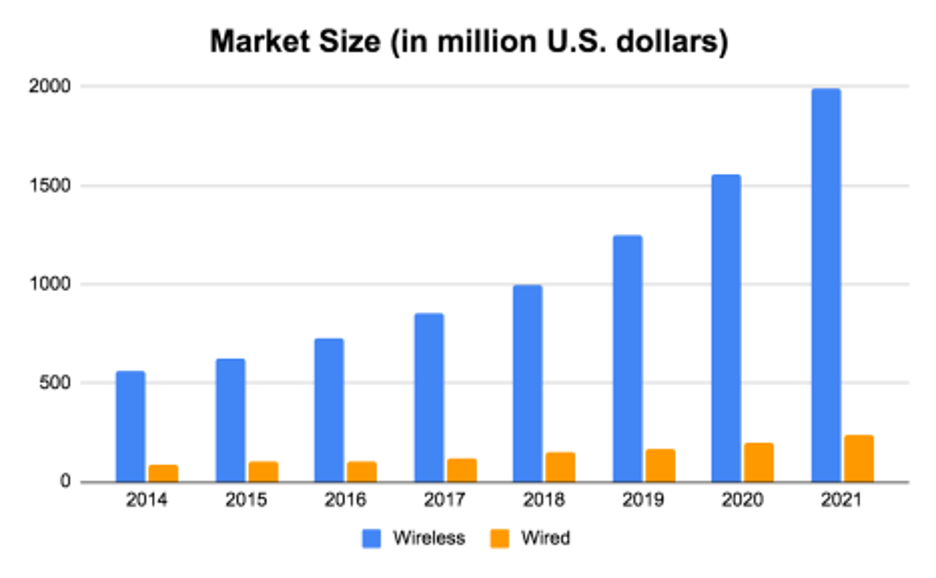
As Bluetooth technology continues to improve, wireless connection is expected to improve as well. Like any piece of technology, improvements are endless and companies will be looking to develop the best wireless headphones for their customers. While the demand for wired headphones will remain stable, the demand for wireless headphones will continue growing at a rapid pace (Fig. 6). With wireless headphones accounting for almost 90% of the revenue in 2020, it is clear that the convenience of wireless technology is a key reason as to why people are opting to purchase them over their wired counterparts. Wireless earphones are the future and sooner than later, it will not be a surprise when everyone owns a pair of wireless earphones.
Further Reading
Apple’s ideas behind developing the W1 chip:
Engineering inside wireless earbuds:
A look through the history of various headphone designs:
References
[1] K, Verma, “Headphones Tech: What Does Driver Units Mean?”, Medium, Oct 29, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://medium.com/@odeskavita/headphones-tech-what-does-driver-units-mean-aeb42b70399f# :~:text=A%20driver%20unit%20is%20basically,helps%20improve%20its%20sound%20quality.
[2] “How Do Wireless Headphones Work?”, Synaptic Sound, [Online]. Available: https://www.synapticsound.com/how-do-wireless-headphones-work/#comments
[3] T, Slattery, “What is Modulation?”, Search Networking, Oct, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/modulation
[4] “How does Modulation Work?”, Radio Academy, [Online]. Available: https://www.taitradioacademy.com/topic/how-does-modulation-work-1-1/
[5] D, Dean, “How to Decide Between Wired vs. Wireless Headphones”, The Klipsch Joint, Jan 9, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.klipsch.com/blog/how-to-decide-between-wired-vs-wireless-headphones#:~:text=W ireless%20technology%20is%20more%20expensive,it%20offers%20better%20sound%20quality
[6] O, Tambini, “Wireless Headphones vs True Wireless Earbuds: Which Design is Best For You?”, Techradar, June 15, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.techradar.com/news/wireless-headphones-vs-true-wireless-earbuds-which-design-is best-for-you
[7] “In-Ear vs. On-Ear vs. Over-Ear Headphones”, Audio Advice, [Online]. Available: https://www.audioadvice.com/videos-reviews/in-ear-vs-on-ear-vs-over-ear-headphones/
[8] B, Wolfe, “Best True Wireless Earbuds You Can Buy Right Now”, iDownloadBlog, Oct 10, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.idownloadblog.com/2018/10/10/best-true-wireless-earbuds/
[9] “Smart Headphones Market Analysis By Product (Wired, Wireless) and Segment Forecasts to 2022”, Grand View Research, Jan, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/smart-headphones-market




